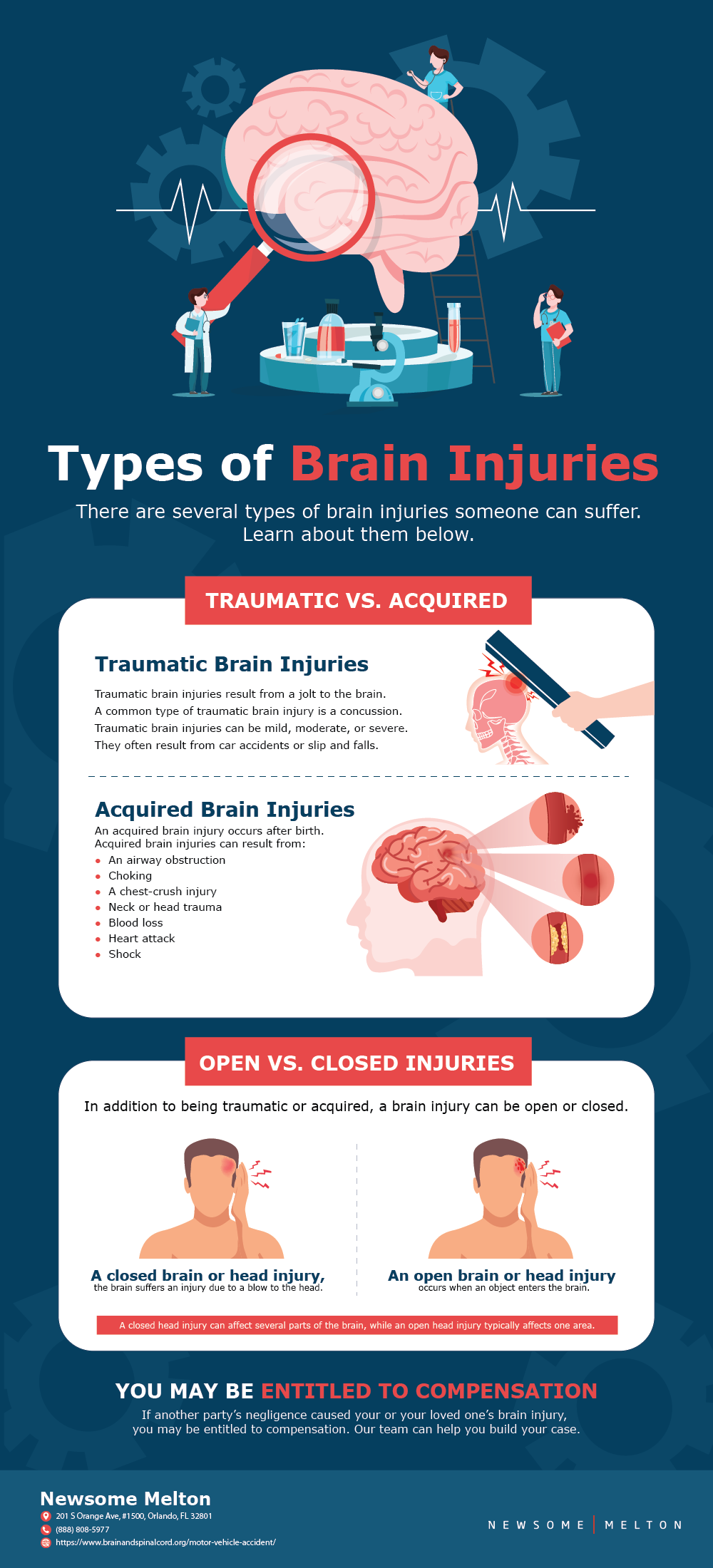
A traumatic brain injury can occur when the head is stricken, suddenly jerked, or penetrated by a foreign object. The injury can be in the range of mild to severe. During a mild brain injury the loss of full conscious awareness will persist for a short amount of time. When a severe brain injury is inflicted there will be memory loss or extended unconsciousness for a prolonged period of time after the injury was inflicted. 1.4 million Americans are reported to sustain a traumatic brain injury every year.
In 2006, a study was done at the Atlanta Nation Center for Injury Prevention and Control. This study showed that of those 1.4 million people, 280,000 people in the U.S. receive a motor vehicle induced traumatic brain injury every year. Twenty percent of all brain damage is motor vehicle related and constitutes as the second largest method. The leading cause is falling, which accounts for 28 percent. However, the traffic accident brain damage accounts for the greatest number of hospitalizations.
Whiplash can be very damaging for the brain. When the head is suddenly twisted with the deceleration of an automobile crash, the brain will move around as well. Billions of nerve cells communicate with other distant cells through long nerve fibers. These delicate fibers can be stretched during an accident, damaging the ability for cells to communicate with each other. Severe whiplash will result in Diffuse Axonal Injury and can potentially put the victim in a coma. With high speed crashes isotropic stress can damage the internal structure of a cell resulting from the density change within the cells. Pressure waves will move through the brain at excessively high speeds. Relatively little research has been done on isotropic stress, but because of the influx of Iraq veterans returning from war with this type of brain damage inflicted by explosives, a large amount of new research will be coming in soon.
The brain is floating with the skull, when the head is bounced around in a motor vehicle accident the brain will not just sit there. It will smash into the walls of its cage, becoming bruised and torn. When the skull strikes the steering wheel, window, concrete, or wreckage the skull will collide against the inside of the skull with much force. The brain continues to move after the head has stopped causing bruising and bleeding at the part of the brain near the point of impact. This point of injury will normally be the frontal lobe (emotional control system) and temporal lobe (selective attention system). After hitting the front of the skull, the brain can bounce back and slam against the back of the skull. This can sometimes damage the occipital lobe which is responsible for visual processing.
Different types of brain injuries include:
Loss of Consciousness – Loss of conscious awareness can span from being slightly dazed to being in a coma for multiple days. To receive permanent damage to the brain, in most cases it is necessary that the victim looses consciousness. The longer the period of unconsciousness, the more severe the brain damage will be.
Post Traumatic Amnesia – Memory loss of events before (retrograde amnesia) and after (anterograde amnesia) the injury was inflicted. Generally the longer the periods of amnesia, the greater the damage will be. If a patient is suffering from amnesia, they will have a difficult time gauging the true extent of their problem. Family members or friends should help track their progress.
Concussion – Altered awareness after trauma to the head. Some symptoms include dizziness, nausea, disorientation, and forgetfulness. Most cases will be resolved within a couple months.
As a result of the direct trauma, secondary injuries can occur in the brain. When tissue is injured or a blood vessel is torn, a collection of blood can build up within the skull. This is called hematoma and the bleeding can occur days after the injury was inflicted.
Edema is when swelling occurs inside of the brain causing a rise in intracranial pressure. Circulation will be damaged and blood will have difficulties delivering important molecules to the brain. Medication can help relieve the pressure, but if that doesn’t work some fluid can be drained out by drilling a hole in the patient’s skull.
There are simple strategies that can be implemented which will greatly reduce the chance of experiencing the horrible realities of a traumatic brain injury first hand. Every time when riding or driving in a motor vehicle, wear a seat belt. This will prevent the body from flying into the window or steering wheel in the event of an accident. Have a child safety seat available for any children who may travel in the vehicle. If the child does do not reach the height and weight requirements, a seat belt will be of no proper benefit. The inertia that has built up can be fatal when the child suddenly hits the back of the driver’s seat.
Driving under the influence of any type of drug or alcohol, whether illegal or legal, will greatly reduce the users awareness of what is going, reducing the quality of driving and the safety for all of the other beings who travel upon the drivers path. When riding a motorcycle, ATV, or scooter, always wear a helmet. By practicing these few simple strategies traumatic brain injury can be greatly reduced or avoided all together.

